Spotting before period, though is a common occurrence during menstrual cycle, can be an early indicator of certain health conditions. Understanding the underlying causes of this symptom can help you gain a better understanding of what is happening to your body and react to it in a right way.
What is Soptting?
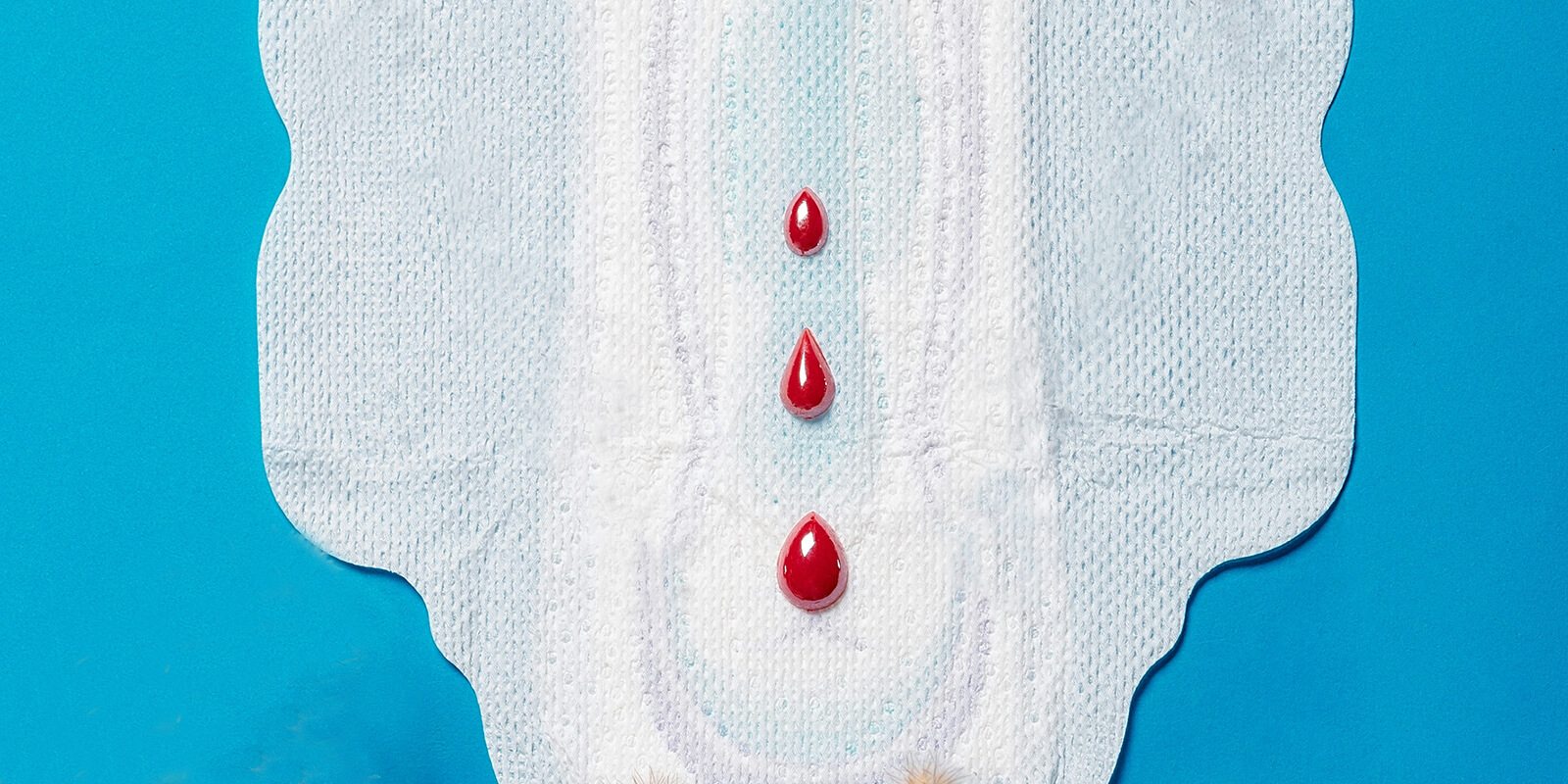
Spotting refers to light vaginal bleeding that occurs outside of a typical menstrual period. It often manifests as small amounts of blood, appearing as pink or brown discharge. Unlike regular menstruation, spotting is characterized by its lightness and brevity. It can occur at various times throughout the menstrual cycle, including before or after periods, during ovulation, or due to hormonal changes.
What Causes Spotting Before Periods?
From hormonal fluctuations to lifestyle factors, various elements can contribute to spotting before periods:
Hormonal Fluctuations:
Throughout the menstrual cycle, the body undergoes hormonal changes, particularly in estrogen and progesterone levels. These fluctuations can sometimes prompt the uterine lining to shed irregularly, resulting in spotting.
Hormonal Birth Control:

Birth control methods such as as pills, patches, or intrauterine devices (IUDs) can cause hormonal imbalance and lead to spotting between periods. If you are using these birth control methods, have tests of certain hormonal levels (like LH, estrogen, and progesterone levels) is essential for you to find a solution to hormonal imbalance.
Ovulation:
Mid-cycle spotting may occur due to ovulation. This typically happens around the middle of the menstrual cycle when an egg is released from the ovary. Some individuals may experience light spotting or bleeding during this time, known as ovulation bleeding.
Recommend Ovulation Tracker: Femometer Smart Ring
Early pregnancy:
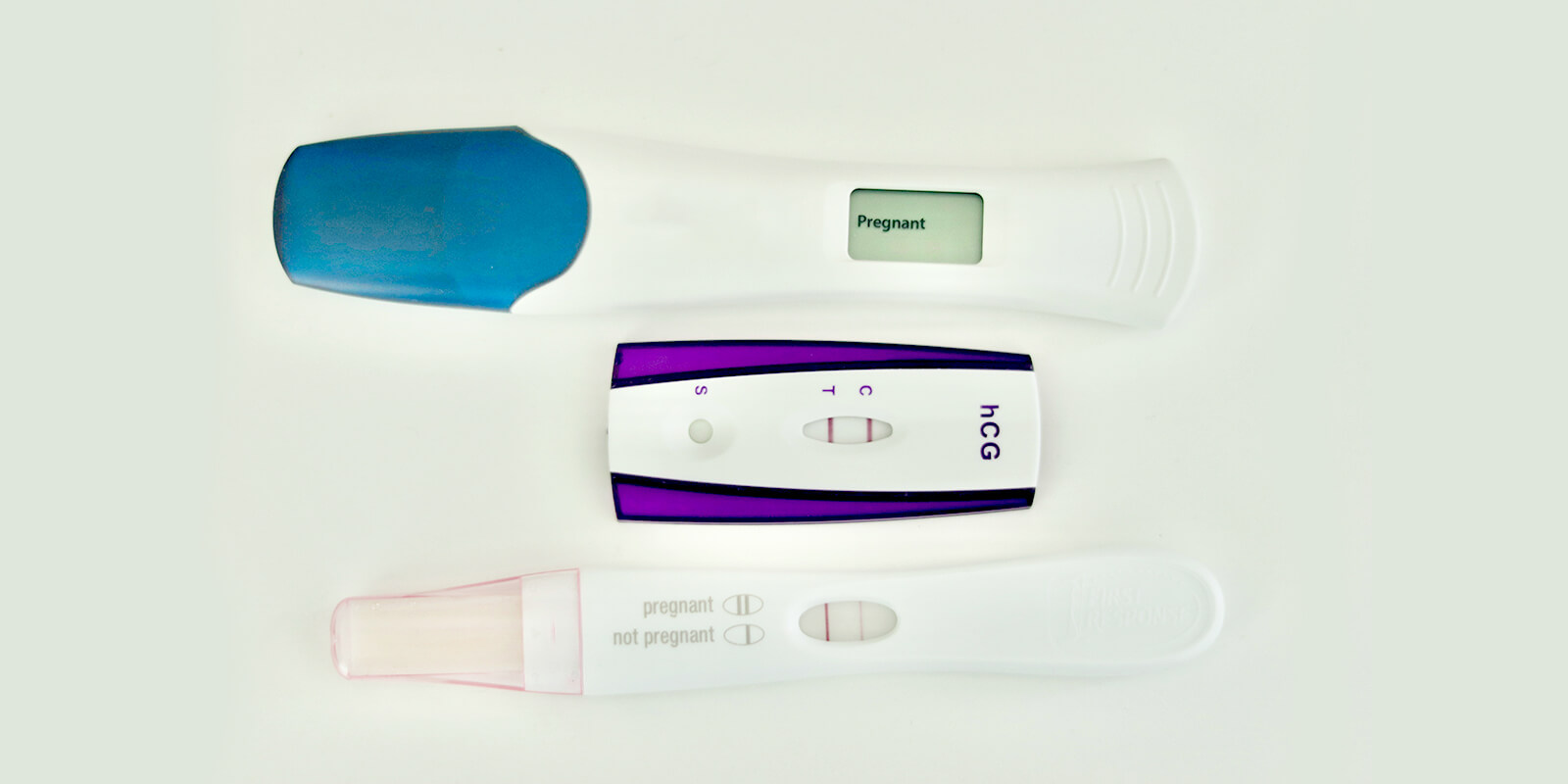
15 to 20 percent of people experience spotting during the first trimester. In early pregnancy, implantation bleeding may occur when the fertilized egg implants in the lining of the uterus, resulting in light spotting, which can be mistaken for the start of menstruation. While spotting is common in early pregnancy, if the bleeding is heavy and accompanied by pelvic pain, it is important to contact your doctor as this can be a sign of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy.
Infections and STIs:
Infections such as gonorrhea, chlamydia, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can cause inflammation and irritation of the cervix or uterus, resulting in spotting or abnormal bleeding before periods.
Lifestyle Factors:
Stress, poor diet, excessive exercise, or sudden weight changes can disrupt hormonal balance and menstrual cycles, leading to irregular bleeding patterns including spotting before periods.
Uterine Fibroids:
Noncancerous growths in the uterus known as fibroids can cause irregular bleeding, including spotting before periods.
Endometriosis:
This condition occurs when the tissue lining the uterus grows outside of it, leading to irregular bleeding and spotting.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS):
PCOS can cause hormonal imbalances that disrupt menstrual cycles, leading to irregular bleeding patterns.
Thyroid Disorders:
Thyroid conditions such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can affect hormone levels and menstrual cycles, potentially causing spotting before periods.
Medications and Medical Treatments:
Certain medications or medical treatments can affect menstrual cycles and cause spotting. For example, anticoagulants, hormone therapy, or chemotherapy can disrupt the normal functioning of the reproductive system, leading to irregular bleeding.
Spotting before periods can stem from various factors, including hormonal fluctuations, ovulation, infections, lifestyle factors, underlying health conditions, medications, or medical treatments. While occasional spotting is usually nothing to worry about, persistent or abnormal bleeding needs your attentions. If spotting is accompanied by pain, unusual discharge, or persists for an extended period, it's advisable to seek medical advice to rule out any underlying health issues.
This article is the original creation of Femometer. All rights reserved by Femometer Inc. To reproduce, distribute, or reference the content, please reach out to us in advance to prevent any potential legal issues. Copyright © Femometer Inc.